| Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are driven by two power plants:
a conventional combustion engine and an electric motor. Depending
on the structure of the system, HEVs can be classified into series
and parallel HEVs.
1. Series HEV
2. Parallel HEV
3. Series-parallel HEV
4. Power-split HEV
Series-parallel HEVs and Power-split HEVs are essentially variations
of parallel HEVs,
but they are nevertheless classified separately according to their
particular features. The development of deceleration and braking
technologies and systems for regenerating energy are being carried
out to still further reduce the emission gases and increase the
fuel economy of these vehicles.
a. Series HEV
The Series HEV is designed to power a vehicle with an electric motor
through the electricity generated by an engine dynamo in the EV.
The engine is only used to generate power and does not directly
transmit a driving force to the drive axle. There are two types
of Series HEV. One is a range extender and the other one is independent
system.
b. Parallel HEV
The Parallel HEV has two sources of energy for driving the axle.
The combustion engine and the electric motor can drive the axle
independently or together.
For example, the zero-emission EV system is run when driving in
small city areas or when going on short trips. Large power outputs
are generally not required in these situations. The conventional
combustion engine is required when running at high-speed between
cities.
c. Series-parallel HEV
Series-parallel HEVs have the functions of both the Series HEV and
the Parallel HEV. Figure 3.31 shows a Series-parallel HEV's changeover
controller.
The drive line is composed of an engine, a first clutch, a second
clutch, a transmission, an electric motor in the rear transmission,
a battery, an inverter, and a rear motor for the rear-wheel-drive
system.
A) Series mode: the engine will power the drive system only when
the first clutch is on and the second clutch is off.
B) Series-parallel mode: both clutches are on. Because the second
clutch is on, engine torque is applied to drive the front wheels
through the transmission.
C) High-speed engine drive system mode: the first and second clutches
are both on, but the electric motor in the vehicle's engine drive
will only drive the front wheels mechanically. This system is more
efficient than the hybrid system and is used when traveling at high-speed
or when carrying heavy loads.
d. Power-split HEV
Power-split HEVs have functions similar to those of Series-parallel
HEVs. However, Power-split HEVs differ in that is branch engine
output uses planet gear. Toyota has been marketing this system in
its Prius since 1997.
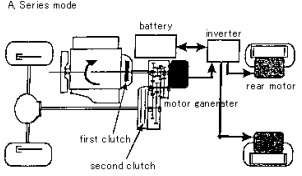 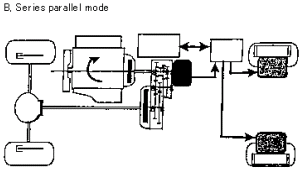
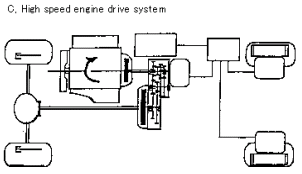 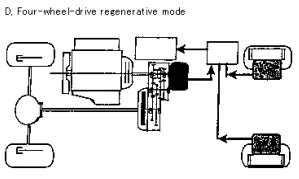
Figure 3.31Å@MItsubishi Motors NEDO-ACE HEV changeover controller
Reference
Book title: EV Handbook
Written by: EV Handbook Publisher's Group
Published by: Maruzen Co., Ltd. (URL http://www.maruzen.co.jp)
|