| Automotive air conditioner |
|
Functions and features of air conditioner
An automotive air conditioner cools, heats, and dehumidifies the interior: it also defrosts the windows, which not only maintains the visibility of the windshield, but also maintains the interior comfortable.
An electric vehicle has no internal combustion engine, and in general the amount of heat radiated by the driving motor and battery is limited. The energy source for the electric vehicle air conditioner only relied on electric energy stored in the main battery.
As a result, the electric power consumption of the air conditioner significantly affects the driving range. Accordingly, the air conditioner for the electric vehicle is required to maintain the passengers comfortable and visibility of the glass with minimum power consumption.
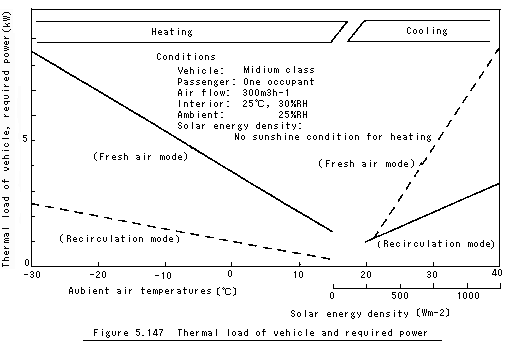
The relationship between the thermal load of a vehicle and its necessary heating/cooling capability is the same as that of an internal combustion engine vehicle. As shown in Fig. 5.147, significant electric power is required to heat the interior at low outside temperatures.
This is due to the fact that fresh air mode, in which low absolute humidity is drawn to prevent the glass from fogging up while the interior is heated, is used.
Vehicle thermal load reduction
1) Thermal load reduction while heating
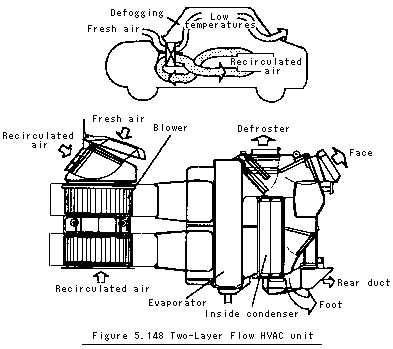
The two-layer HVAC (heating ventilation and air conditioning) unit is applied to reduce the thermal load for heating especially when the outside air temperature is very low. It is also used for a hybrid vehicle without a heat source and/or high efficiency internal combustion engine. The unit, shown in Fig. 5.148, is used for electric vehicles.
The air passage is divided into two layers. Low humidity fresh air which is heated through the condenser is drawn into the upper layer, then blown out to DEF vent along the windshield. Simultaneously, the recirculated air which is heated through the condenser is drawn into the lower layer and blown toward the passenger's feet to the vehicle interior. This two-layer flow HVAC can reduce the amount of fresh air to 25 to 50%, and heat the thermal load to 50 to 66%, resulting in a substantial reduction of electric power consumption.
2) Thermal load reduction while cooling
In the recirculation mode, half of the thermal load is caused by solar radiation through the window glass. To reduce thermal load caused by solar radiation, glass that deflects or absorbs solar energy is used. By using these glasses, approx. 50% of the thermal load caused by solar radiation can be reduced.
Reference
Book title: EV Handbook
Written by: EV Handbook Publisher's Group
Published by: Maruzen Co., Ltd. (URL http://www.maruzen.co.jp)
|
|