| The application of DC/DC converter to the vehicle |
|
A careful examination of output current and output voltage is needed to provide a proper DC/DC converter
which results in a good balance between the vehicle charge and discharge and prevents the battery
from going dead. In addition, selecting a DC/DC converter with optimum capacity is also necessary
for downsizing and cost reduction.
1) Output current: The output current required from the vehicle depends on auxiliary load capacity and
frequency of use according to the running conditions. It is important to estimate the running condition
for output current requirement. Therefore, we will explain how to determine an output current of DC/DC
converter in comparison with that of alternator. Fig. 5.138 shows an example of the frequency distribution
of engine revolution speed while running on urban roads, which also shows an output current of alternator
according to the engine revolution speeds. Since the alternator is driven by the engine, the output current
increases according to the engine revolution speed. The current supply capacity of the alternator Ie (A) is
expressed by the following equation, where ă1(%) represents the in use of the engine revolution speed
N1 (min-1), and I1 (A) represents the occurrence current.
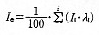
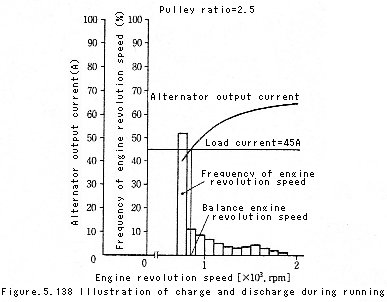
For example, when the load current is 45 A, the alternator output current is 40 A at an idle revolution speed
of 700 min-1. Consequently, the amount of undercurrent is compensated for by discharging battery. The battery can
be recharged when the engine revolution speed additionally increases by achieving a balance between the load current
and the alternator output at an engine revolution speed of 800 min-1.
The ways to determine the alternator output current taking into consideration the running conditions are as follows.
- Setting the maximum output to 130 to 150% of the nighttime normal use load
- Setting the output while idling at more than a required current of the ignition and fuel systems
- Setting the output while running at a vehicle speed of 40 to 50 km/h in top gear at more than a load of nighttime normal use load
- Setting the effective output while city mode running at more than a load of a nighttime normal use load.
In contrast to this, since the DC converter can constantly supply the maximum output current independently of the
engine revolution speed, evaluations made under the running patterns of 2), 3) and 4) above related to running
conditions are of little importance. Consequently, consideration shall be given mainly to the nighttime normal use
load which requires the greatest current.
2) Output voltage: It is necessary to determine an output voltage taking into consideration the auxiliary battery
characteristics and vehicle wiring etc, as in the case of the alternator. However, the common method is to decrease
the output voltage according to the increase in the auxiliary battery temperature in order to provide the auxiliary
battery life and to improve charging conditions in cold weather. In addition, for electric vehicles, the output voltage
is switched while running and charged to increase the travel distance between battery recharges.
The auxiliary batteries are fully charged by setting the output voltage at a little high when recharging the main
battery, considering an overall balance between charge and discharge of the auxiliary batteries while running and charge.
On the other hand, setting the output voltage at a little low while running decreases the drain on the main battery.
Reference
Book title: EV Handbook
Written by: EV Handbook Publisher's Group
Published by: Maruzen Co., Ltd. (URL http://www.maruzen.co.jp)
|
|